Details of VNET Plus:
Advantages of VNET Plus:
-
- - It enables you unconstrained P2P communications even if there exist several NATs (Network Address Translation devices) on the communication routes. This means that you will never face the "NAT traversal problems" during communicatiion.
- - A communication route is surely established if you just specify the name of the other party.
- - Authentication and encryption processes are executed between end communication devices.
- - Communication can be maintained even if the network used by the device is switched to another network during the communication.
- - The most suitable communication route will be established with the least delay.
- - You can build a closed communication group by defining at the management server.
- - Original types of countermeasures against DoS attacks are taken.
- - The encryption key is kept unknown even to the network administrator.
- - The network configuration under NAT is hidden in the same manner as that for the actual network.
- - The definition of communication grouping can easily be set without any special knowledge.
- - You can use the existing applications as they are without making any change.
- - There is no need for you to change the existing network configuration.
- - You can make VNET Plus communications and normal communications at the same time.
It must be noted, however, that the communication devices need to be connected to a TCP/IP network and also that it is necessary for you to set a system to pass through UDP port 4330 in the case of the environment with some firewalls.
Specifications of VNET Plus:
The black letters are realized in the initial release, while the red letters are realized in the subsequent releases.
-
Communication functions:
- Unconstrained mutual communications in IPv4 areas without the necessity of being aware of the existence of NATs are possible.
- Unconstrained mutual communications in the environment of a mixture of the IPv4 / IPv6 networks are possible.
- Mobility is possible. -
Communication route:
- Basically, P2P direct communication route is established. However, communications via TS are established in the following cases.
- - When one device is connected to IPv4 while the other is connected to IPv6.
- - When both end devices are connected under Symmetric NATs.
- - Configuration is based on a special multi-staged NAT.
-
Security:
P2P packet authentication and encryption processes are undertaken.
(AES256 bit, SHA256)
Countermeasures against DoS attacks and those against replay attacks are adopted.
Communication grouping is realized.
The encryption keys for communications are kept unknown even to the administrator. -
User’s authentication:
An extended password method (multi-factor authentication using a random number) is applied.
-
Scalability:
Distributed arrangements for DC as well as for TS are adopted.
-
Coexistence with general communications:
It is possible to co-exist with general communications.
VNET Plus Security:
VNET Plus is extremely secure for the following reasons.
- - All packets related to VNET Plus are encrypted and an authentication code is applied to each of them to prevent from tampering.
- - As the encryption key that encrypts packets between end devices is unknown to the administrator, there is no need for you to worry about information leakage from the administrator.
- - It provides a closed communication group that allows mutual communications strictly within the same group.
- - It has its own DoS attack countermeasures that detect and discard malicious packets at a high speed.
- - Perfect countermeasures against replay attacks are also provided.
- - VNET Plus adopts the encryption algorithm AES CBC mode with a key length of 256 bits and the hash algorithm SHA256, whose security is guaranteed at the present time.
Product types:
1 The VNET Plus application
The following OS's can be used for the VNET Plus application.
- - Linux (Ubuntu20.04lts and its later versions, Raspbian 64-bit)
- Windows 10
- Android
- iOS
2 VNET Plus Adapter:
In the case where you use a device with any unsupported OS, or in the case where you do not want to change the existing devices at all, you can use VNET Plus Adapter.
As for the details, please refer to the "How to use VNET Plus".
- VNET Plus Adapter Type C:
It needs to be set on the side of the communication device such as a client terminal that initiates communication.
- VNET Plus Adapter Type S:
It needs to be set on the side of the communication device such as a server that awaits communication.
How to give VNET names:
About FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name):
In order to use VNET Plus, it is necessary to give a name to each applicable communication device.FQDN is normally the name given to a server to be used on the Internet.
The FQDN rules ensure that every name is unique throughout the world.
The name given to the VNET Plus device conforms to the FQDN, and the name must end with letters ” .ntm20.com”.
For example, the name of your VNET Plus device is given like below.
VNET Plus name: aaa.abc.ntm20.com
If the device is a web server, it could already have the FQDN like below.
Web server name: aaa.abc.acompany.co.jp
In that case, you leave the conventional FQDN as it is and simply add the FQDN for VNET Plus.
If the device is a client, it usually does not have FQDN.
In this case, a new FQDN for VNET Plus needs to be given to the client.
When the client enters the web server name (aaa.abc.ntm20.com) and the file name in the URL field of the browser, the contents of the server can be browsed in the same manner as before.
In the case where you have been accessing your server by inputting the name reading
http://aaa.abc.acompany.co.jp/document.html
in the case of VNET Plus accessing the same file.
http://aaa.abc.ntm20.com/document.html
Subdomain name:
The abc part of the FQDN of VNET Plus is the domain name to identify the user organization.The representative person of a group of users has to obtain a subdomain name from the "User Registration" tab.
The representative person has to assign an FQDN including the acquired subdomain name to each of the end users.
The aaa part is user specific, and can be further layered like aaa.bbb.
Communication group:
Communication group names are also required for the VNET Plus networks.At least one group name needs to be assigned to each unit of the VNET Plus devices.
Only the devices having the same group name can communicate with each other.
No special rules exist concerning the group names.
Devices can belong to a number of different groups.

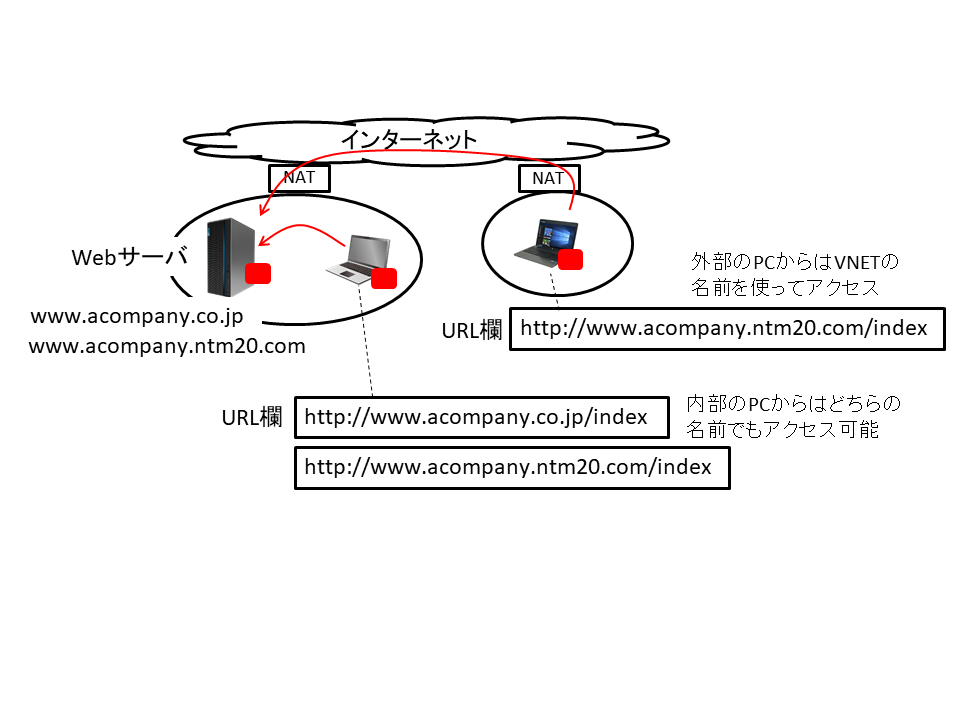
The figure below shows an example of how to get access to the web server in the company from internal and external PCs securely.
The web server can be accessed using either of the traditional name or the VNET Plus name.
P2P communication security is guaranteed when accessed with the name of VNET Plus.
External PCs such as home PCs can get access to the web server in the company by using the VNET Plus name.
You do not need to be concerned about the existence or non-existence of NATs, and you can access the server with exactly the same way as the PCs in the company.
Development of new communication applications:
By using VNET Plus, you will be able to develop new communication applications based on your new ideas.
Thus far, limited types of network systems such as the client/server system have been realized due to the restrictions from the existence of NAT.
However, with the introduction of VNET Plus, it is no more necessary for you to take any network restrictions into account.
From the perspective of communication devices, the virtual IP network realized by VNET Plus will be indeed just like a huge LAN that straddles across the world.
Information can be freely exchanged between end devices by way of P2P.
If and when the environment is more suitable for the client/server type system, a server can be set in any areas such as in the private address area which is more secure than the Internet.
Information can be freely exchanged between servers even if they are in private address areas.
The devices can also be established as a secure communication group isolated from other communication systems.

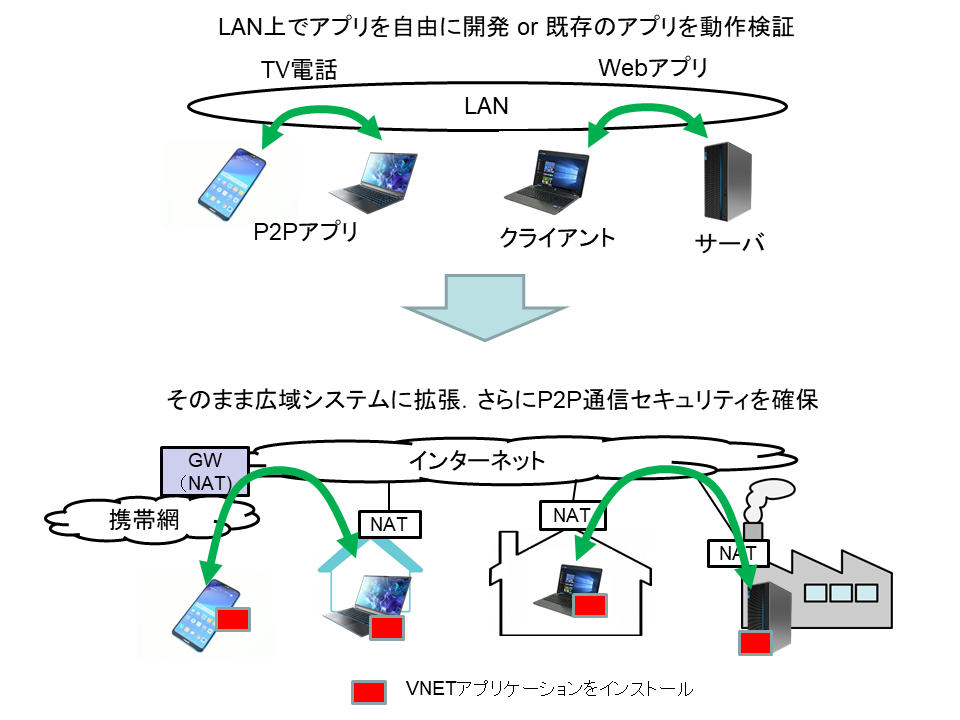
You will be able to develop and verify your system by taking the following steps.
(1) Build an application on the LAN and verify its operation.
(2) Install the VNET Plus application on each communication device.
Then, it becomes possible for you to migrate to a system with wider areas that straddles over the Internet.
The already proven systems in LAN can also be used as they are.
You should take into account the following matters when developing a new application.
- You keep in mind the fact that VNET Plus will remove all network constraints.
- What you have to do is just to develop a system that runs on a LAN.
- As VNET Plus solves the NAT traversal problem, you can forget about the existence of NATs.
- Although there exist technologies called STUN/TURN as a NAT traversal means, you should not use these technologies together with VNET Plus because they compete with the functions of VNET Plus.
- As VNET Plus hides the real IP address from the application, there exists a possibility that the relationship between the virtual IP address and the real IP address is confused and safe operation cannot be guaranteed as the result, if the application is designated with the real IP address in mind.
- VNET Plus starts operation by the name resolution protocol based on DNS as a trigger. Thus, the name resolution using LAN broadcasting such as Multicast DNS cannot be used.
Performance:
VNET Plus is equipped with a high communication performance.
In our experiment, the TCP throughput of VNET Plus was measured as follows.
- Linux PC (Core i5, 2.7GHz Ubuntu 20.04LTS): 220Mbps
- Raspberry pi 4 : 67Mbps
Measurement conditions:
- 1000BASE-TX wired direct connection
- PC specifications: Core i5, 2.7GHz Ubuntu20.04LTS
- Measurement tool: iperf
If and when the networks in use are switched during the communication, the time required for the resumption of communication is less than 1 second.